 The female flea feeds by burrowing into the skin of its host. The abdomen becomes enormously enlarged between the second and third segments so that the flea forms a round sac with the shape and size of a pea.
The female flea feeds by burrowing into the skin of its host. The abdomen becomes enormously enlarged between the second and third segments so that the flea forms a round sac with the shape and size of a pea.
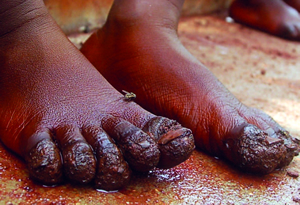
The impregnated female Tunga embeds itself in the skin under the toenails and fingernails of man – where the resultant sores may fill with pus and become infected. Others victims can be dogs, cats, rats, pigs, cattle and sheep.
The first evidence of infestation by this sand flea is a tiny black dot on the skin at the point of penetration. Because the flea is a poor jumper, most lesions occur on the feet, often on the soles, the toe webs, and around or under the toenails. A small, inflammatory papule with a central black dot forms early. Within the next few weeks, the papule slowly enlarges into a white, pea-sized nodule with well-defined borders between 4-10mm in diameter. This lesion can range from asymptomatic to pruritic to extremely painful. Multiple/severe infestations may result in a cluster of nodules with a honeycomb appearance.
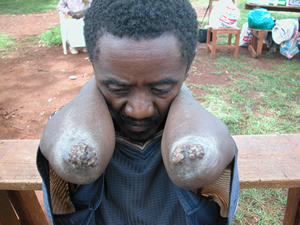
Heavy infestations may lead to severe inflammation, ulceration, and fibrosis. Lymphangitis, gangrene, sepsis, the loss of toenails, autoamputation of the digits, and death may also occur. In most cases, however, this lesion heals without further complications.
Nonetheless, the risk of secondary infection is high. Tetanus is a common secondary infection that has reported associations with death.